Tulkubash
Tulkubash is an oxide gold deposit suitable for open pit mining and extraction using standard heap leach gold extraction technology.
It has a well drilled JORC compliant proven and probable reserve which enabled a comprehensive Bankable Feasibility Study (“BFS”) update report in which has been reviewed by external parties. A significant amount of drilling has occurred in the area, with more than 107,000 meters drilled to date.
The Project is fully permitted for construction and operation and has been developed in accordance with international environmental and social standards.
The project has been significantly de-risked with EPC, O&M and Mining contracts signed with Power Construction Corporation of China Limited, the Kyrgyz subsidiary of Power Construction Corporation of China International Group Limited (“Power China”) in October 2023.


Key facts
- Open Pit Mine type
- 95koz/pa Production
- 1,011koz/Au Resources (MRE 2022)
Project Economics
| Au | Ag price (USD/oz) | 1,450 / 17.5 | 1,700 / 22.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Ave Project Cash Flow p.a. | 44 | 55 |
| LOM Project Cash Flow incl. CAPEX (USDm) | 134 | 199 |
| NPV5% (USDm) | 85 | 135 |
| Post-tax IRR | 25% | 35% |
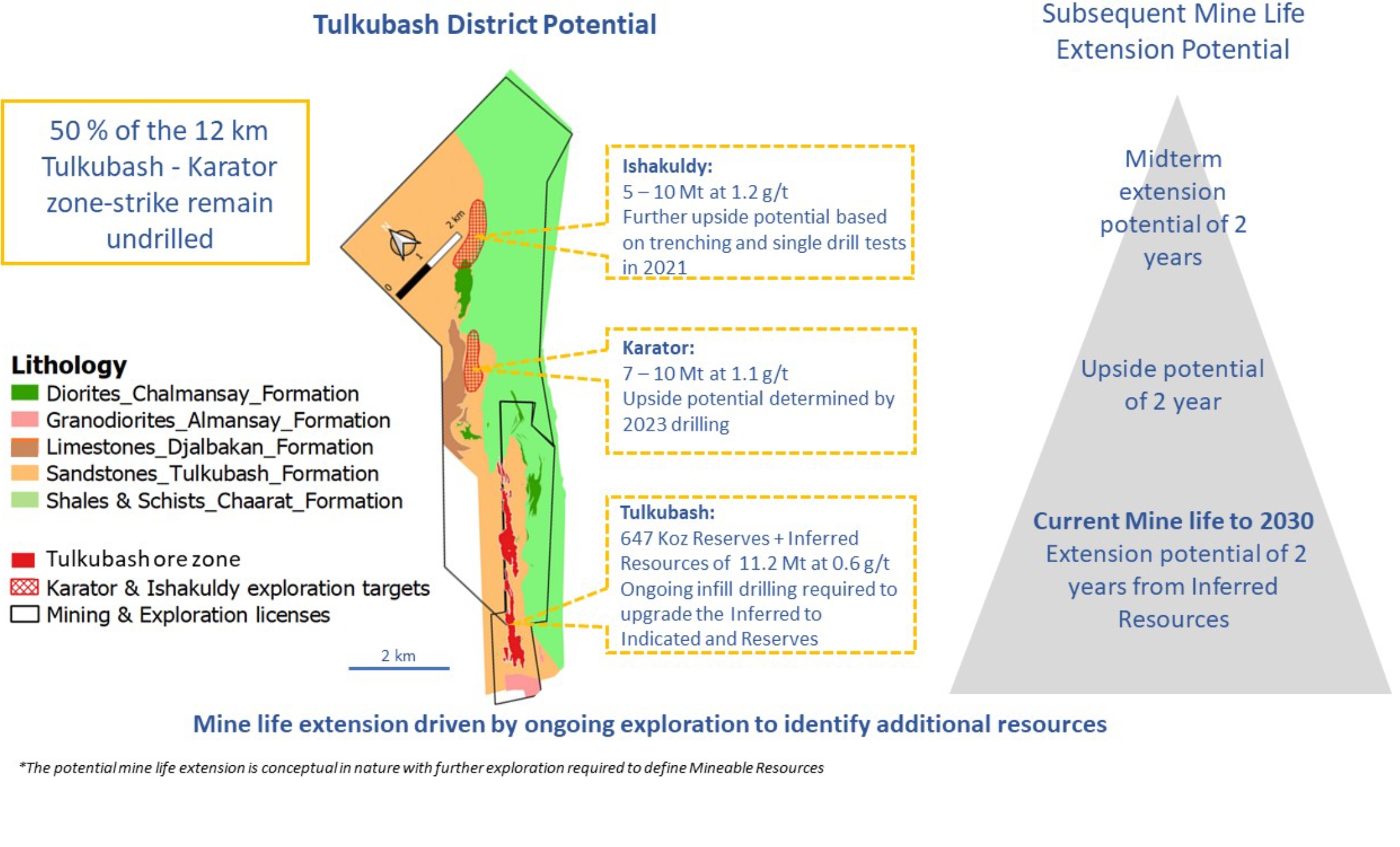
Resource Upside
Environment
- Project fully compliant with Kyrgyz legislation and international best practice, fully permitted for construction
- During operations ongoing monitoring work will be performed in accordance with national and international standards.
- Chaarat has developed an Emergency Preparedness and Response Plan (EPRP) for the Project with a dedicated HSE Manager. HSE department will consist of safety engineers, environmental engineer and specialists, avalanche and rescue team and medical team.
- In Chaarat’s main office in the Chatkal Valley, Chaarat hosts stakeholder meetings and maintains a grievance register.
- Due to the distance of the nearest communities from the Mine site, any negative socio-economic impacts to the Mine are likely to be limited.
- It is anticipated that the positive impacts from employment and community investment on the local communities will be significant.
- Initially, there will not be any groundwater inflow. After full ramp up, water will be managed in accordance with the site wide water balance plan
- Noise impacts on local communities are predicted to be significantly below noise levels per international guidelines.
- Main air emissions are expected to be dust from haulage vehicles operating on unpaved roads and combustion emissions from site operations and haulage vehicles. The ESMS includes several mitigating measures that will be implemented by Chaarat.
Tulkubash – Mining
- The Tulkubash deposit will be developed and mined using conventional hard rock open pit mining techniques
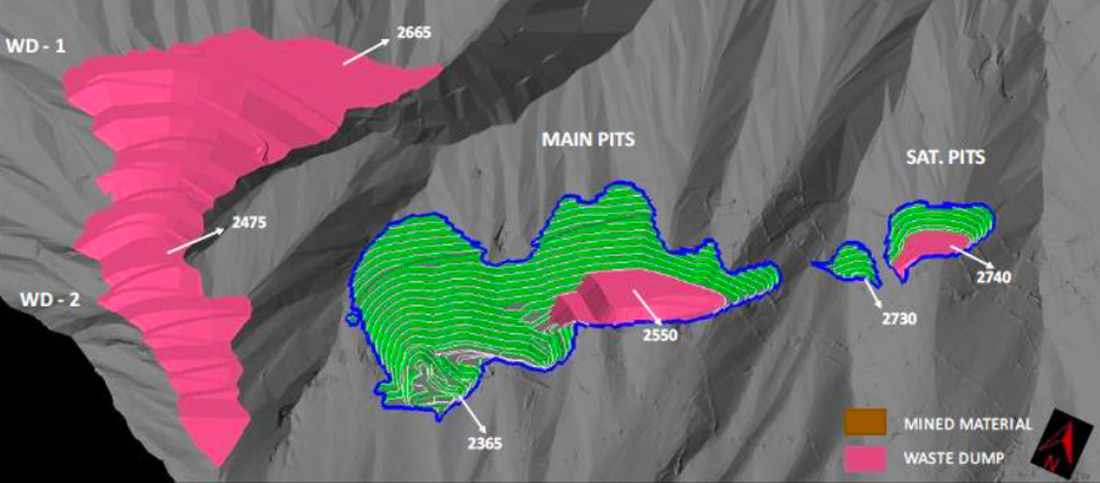
- The open pit design is composed of three separate pits arranged along the strike of the orebody. The deposit is divided up into two zones, the Main Zone and the Mid Zone.
- The Main Zone Pit is the singled largest pit situated at the SW end of the mining area. The Main Zone Pit is approximately 1.3km in length and accounts for over 90% of the mineral reserves at Tulkubash
- The Mid Zone Pit is composed of two separate small open pits
Tulkubash – Metallurgy & Processing
- Processing at Tulkubash consists of a conventional three-stage crushing circuit which will crush the run-of-mine (ROM) ore.
- Trucks then haul the crushed ore to the heap leach pad where it will be stacked in a permanent multi-lift heap leach.
- Lifts will be irrigated with a dilute cyanide solution to dissolve the gold and silver from the ore into the solution.
- Once the solution reaches the base of the heap, it will flow to the pregnant solution pond. From there it will be gravity fed to the ADR plant for gold and silver recovery.
- The precious metals from this pregnant solution will absorb onto granular activated carbon in the carbon columns of the ADR plant.
- The loaded carbon will be pressure stripped with a hot caustic solution to re-dissolve the previous metals into an eluate solution. The eluate will be treated using conventional electrowinning to produce gold-rich sludge suitable for direct smelting on site into gold Doré.
- Gold Doré bars are then transported off-site to a suitable refinery.
Stay in touch
Keep up to date with our news by subscribing to our email alerts